AII-BVI Compounds: ZnTe
AII-BVI Compounds: ZnTe
Description
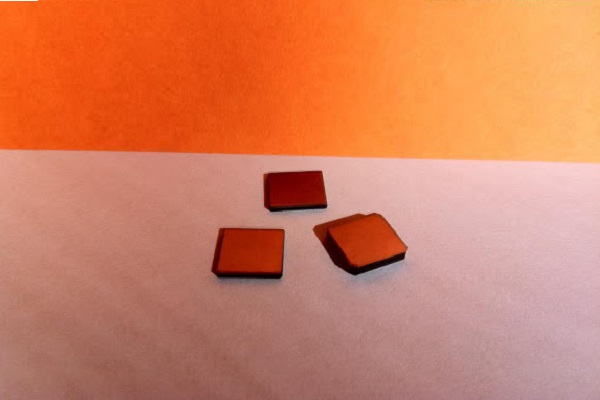
Zinc Telluride (ZnTe) is an AII-BVI compound, which means it is composed of a group II element (Zinc) and a group VI element (Tellurium). It is a semiconductor material with a relatively narrow bandgap of 2.26 eV, which makes it transparent in the infrared region. ZnTe is a useful material for a variety of applications, including optoelectronics, infrared optics, and solar cells. It has a cubic crystal structure and is commonly grown as a single crystal using techniques such as molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) or metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy (MOVPE). ZnTe has a high refractive index and low dispersion, making it ideal for lenses and other optical components operating in the infrared region. It is also used as a substrate for the growth of other semiconductor materials, such as cadmium telluride (CdTe).
| Material | ZnTe |
| Growth methods: | Seeded Vapor Phase |
| Diameter, mm | 40 |
| Thickness, mm | 15 |
| Optical absorption (bulk) at 10,6 nm, cm-1 | - |
| Resistivity, Ohm x cm | 1x106 |
| Luminescent emission intensity ration, IEx/Iedge (Iimp) | - |
| Dislocation density, cm-2 | - |
| Small-angle boundary density, cm-1 | < 10 |
| Excition band wavelength in luminescence spectrum, nm | - |
| The variation of local values for wavelength within the plate, nm | - |
| The number of cavities with size of 15 - 200 m, pcs/pl | - |
Order Form
About Semiconductor Electronics
SEMI EL project is a global supplier of materials, equipment, spare parts and supplies for the semiconductor industry.
Get In Touch
Email: info@semi-el.com

